Knee Anatomy
The knee is a complex joint made up of different structures - bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles. They all work together to maintain the knee’s normal function and provide stability to the knee during movement.
Having a well-functioning healthy knee is essential for our mobility and ability to participate in various activities. Understanding the anatomy of the knee enhances your ability to discuss and choose the right treatment procedure for knee problems with your doctor.
Bones of the Knee
The knee is a hinge joint made up of two bones, the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). There are two round knobs at the end of the femur called femoral condyles that articulate with the flat surface of the tibia called the tibial plateau. The tibial plateau on the inside of the leg is called the medial tibial plateau and on the outside of the leg, the lateral tibial plateau.
The two femoral condyles form a groove on the front (anterior) side of the knee called the patellofemoral groove. A small bone called the patella sits in this groove and forms the kneecap. It acts as a shield and protects the knee joint from direct trauma.
A fourth bone called the fibula is the other bone of the lower leg. This forms a small joint with the tibia. This joint has very little movement and is not considered a part of the main joint of the knee.
Articular Cartilage and Menisci of the Knee
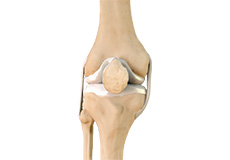
Movement of the bones causes friction between the articulating surfaces. To reduce this friction, all articulating surfaces involved in the movement are covered with a white, shiny, slippery layer called articular cartilage. The articulating surface of the femoral condyles, tibial plateaus and the back of the patella are covered with this cartilage. The cartilage provides a smooth surface that facilitates easy movement.
To further reduce friction between the articulating surfaces of the bones, the knee joint is lined by a synovial membrane that produces a thick clear fluid called synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates and nourishes the cartilage and bones inside the joint capsule.
Within the knee joint, between the femur and tibia, are two C-shaped cartilaginous structures called menisci. Menisci function to provide stability to the knee by spreading the weight of the upper body across the whole surface of the tibial plateau. The menisci help in load-bearing i.e. it prevents the weight from concentrating onto a small area, which could damage the articular cartilage. The menisci also act as a cushion between the femur and tibia by absorbing the shock produced by activities such as walking, running and jumping.
Ligaments of the Knee
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect one bone to another bone. The ligaments of the knee stabilize the knee joint. There are two important groups of ligaments that hold the bones of the knee joint together, collateral and cruciate ligaments.
Collateral ligaments are present on either side of the knee. They prevent the knee from moving too far during side to side motion. The collateral ligament on the inside is called the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the collateral ligament on the outside is called the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
Cruciate ligaments, present inside the knee joint, control the back-and-forth motion of the knee. The cruciate ligament in the front of the knee is called anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the cruciate ligament in the back of the knee is called posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Muscles of the Knee
There are two major muscles in the knee - the quadriceps and the hamstrings, which enable movement of the knee joint. The quadriceps muscles are located in front of the thigh. When the quadriceps muscles contract, the knee straightens. The hamstrings are located at the back of the thigh. When the hamstring muscles contract, the knee bends.
Tendons of the Knee
A tendon is a tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. The quadriceps muscles of the knee meet just above the patella and attach to it through a tendon called the quadriceps tendon. The patella further attaches to the tibia through a tendon called the patella tendon. The quadriceps muscle, quadriceps tendon, and patellar tendon all work together to straighten the knee. Similarly, the hamstring muscles at the back of the leg are attached to the knee joint with the hamstring tendon.
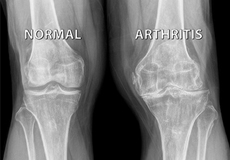
Knee Arthritis
Joint surfaces are covered by a smooth covering called cartilage. This allows pain-free, smooth movement between the bones.

Painful or Failed Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is a surgery employed to resurface knee joints damaged by arthritis, degeneration, or injury and replacing the damaged joints with a prosthesis (an artificial knee joint).

Periprosthetic Knee Infection
A very small percentage of patients (less than 1%) who undergo knee replacement may develop an infection around the knee joint. This infection is called a periprosthetic knee infection.
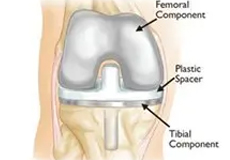
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with an artificial prosthesis.

Revision Knee Replacement
Revision knee replacement surgery involves replacing a part or all your previous knee prosthesis with a new prosthesis. Although total knee replacement surgery is successful, sometimes the procedure can fail due to various reasons and may require a second revision surgery.

Intraarticular Knee Injection
Knee pain and stiffness can be disabling and difficult to treat. It can limit an individual’s lifestyle and negatively impact body image and emotional well-being.


